Phototherapy
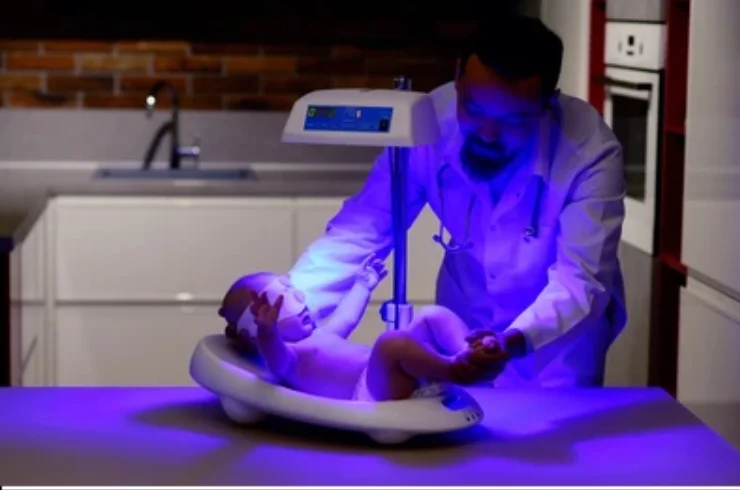
Phototherapy is a medical treatment that uses light to treat various health conditions, most commonly skin disorders and jaundice in newborns. It involves exposing the patient to specific wavelengths of light to either treat or manage a condition. The light used in phototherapy can come from natural sunlight or artificial light sources, such as fluorescent or LED lights, depending on the condition being treated.
Some of the primary applications of phototherapy include:
Neonatal Jaundice: Phototherapy is widely used to treat jaundice in newborns. Jaundice occurs when there is a buildup of bilirubin in the blood, causing yellowing of the skin and eyes. The light helps break down the excess bilirubin into forms that can be excreted more easily by the baby’s body, helping to reduce the yellowing.
Skin Disorders: Phototherapy is also used to treat various skin conditions, including psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo, and atopic dermatitis. It works by exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light, which can reduce inflammation, slow down the overproduction of skin cells, and promote healing. Narrowband UVB therapy is the most common form used for these conditions.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): Phototherapy is used as a treatment for seasonal affective disorder, a type of depression that occurs during the winter months due to a lack of sunlight. Light therapy can help regulate circadian rhythms, improve mood, and alleviate symptoms of depression by mimicking the effects of natural sunlight.
Sleep Disorders: In some cases, phototherapy is used to help regulate sleep patterns, particularly for those with insomnia or other circadian rhythm disorders. Light exposure at specific times of day can help reset the body’s internal clock.
Phototherapy is generally considered safe, but it should be performed under medical supervision to ensure the appropriate type and duration of light exposure, especially in vulnerable populations like infants. Overexposure to light, particularly UV light, can lead to skin damage, burns, or other adverse effects.
